In recent years, automation technologies have become more advanced, accessible, and versatile, substantially impacting various manufacturing sectors. Today, process automation is not just a trend but a necessity for industries striving to stay competitive, agile, and efficient in a fast-paced global market. Automation in manufacturing encompasses a wide range of technologies, including robotics, artificial intelligence, machine learning, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and data analytics. These technologies work harmoniously, creating a seamless network of interconnected systems that optimize production processes, enhance decision-making, and revolutionize manufacturing goods. One of the most notable trends in industrial automation is the integration of collaborative robots or cobots. Unlike traditional industrial robots, cobots are designed to work alongside human operators, assisting with repetitive tasks and increasing productivity without compromising safety. This human-robot collaboration improves efficiency and enhances the work environment, empowering workers to focus on higher-value tasks requiring creativity and problem-solving skills. Furthermore, artificial intelligence and machine learning have emerged as game-changers in industrial automation. These technologies enable machines to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make real-time autonomous decisions. As a result, manufacturing processes can be optimized, predictive maintenance can be implemented, and production bottlenecks can be proactively addressed, leading to increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime. Further, to better understand the significance of industrial automation in manufacturing, let’s look at its key benefits.

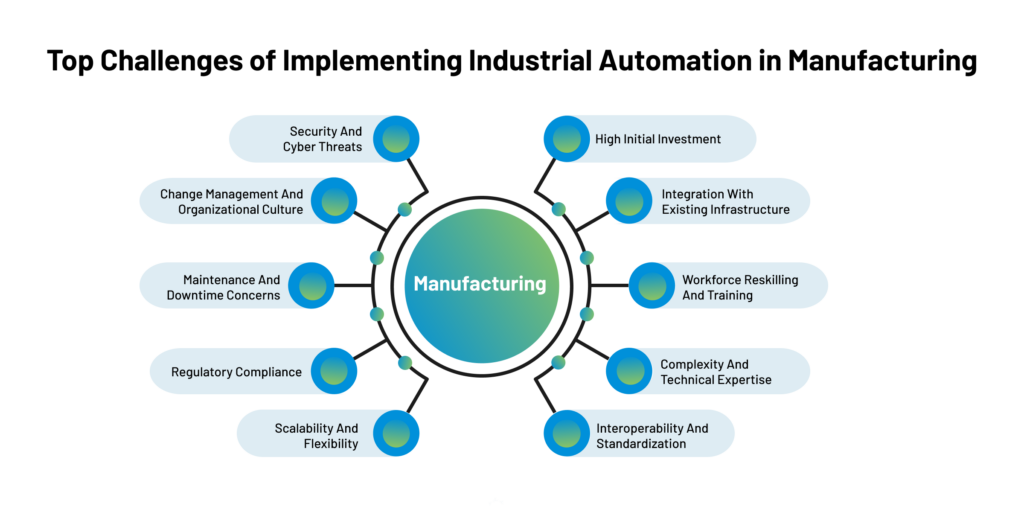
Here are the top challenges of implementing industrial automation in manufacturing: High Initial Investment: The substantial upfront cost is one of the most significant hurdles in adopting manufacturing automation. The required machinery, sensors, robotic systems, and software can be expensive, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Organizations must carefully analyze the return on investment (ROI) and long-term benefits to justify the initial capital expenditure. Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Manufacturers often have legacy systems and equipment not designed with automation. Integrating new automated processes with existing infrastructure can be complex and require additional modifications or retrofits to ensure compatibility and smooth functioning. Workforce Reskilling and Training: Automation can lead to changes in job roles and responsibilities. As tasks are automated, employees must acquire new skills to manage and maintain the automated systems effectively. Training the existing workforce or hiring new skilled personnel can be challenging and time-consuming. Complexity and Technical Expertise: Automation systems can be intricate, involving advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and complex programming. Implementing and maintaining these systems requires a skilled technical workforce with robotics, software development, and data analytics expertise. Interoperability and Standardization: Different automation technologies and equipment from various vendors may need to work seamlessly in a manufacturing environment. Lack of standardization can lead to compatibility issues and difficulties in creating a unified and efficient automation ecosystem. Security and Cyber Threats: As manufacturing facilities become more connected through the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and automation, they also become susceptible to cyber threats. Safeguarding critical data and intellectual property and preventing unauthorized access becomes paramount, necessitating robust cybersecurity measures. Change Management and Organizational Culture: Introducing automation can disrupt the existing work processes and create resistance among employees who fear job displacement or unfamiliarity with new technologies. A well-planned change management strategy and a positive organizational culture that promotes innovation and adaptation are essential to overcome these challenges. Maintenance and Downtime Concerns: Automated systems require regular maintenance and updates to ensure optimal performance. Sudden breakdowns or downtime due to technical issues can severely impact production, making efficient maintenance procedures crucial. Regulatory Compliance: In regulated industries, implementing automation may require adherence to specific standards and compliance with safety regulations. Ensuring the automated processes meet all legal and safety requirements can be demanding. Scalability and Flexibility: Manufacturers must consider the future scalability of their automation systems to accommodate changes in production demands and technological advancements. Ensuring the automation setup remains flexible enough to adapt to evolving business needs is a constant challenge. Addressing these challenges requires a well-thought-out strategy, collaboration between different departments within the organization, and a willingness to embrace technological advancements while considering the workforce’s well-being. With careful planning and execution, industrial automation can significantly enhance manufacturing processes and competitiveness. How? Let’s look.
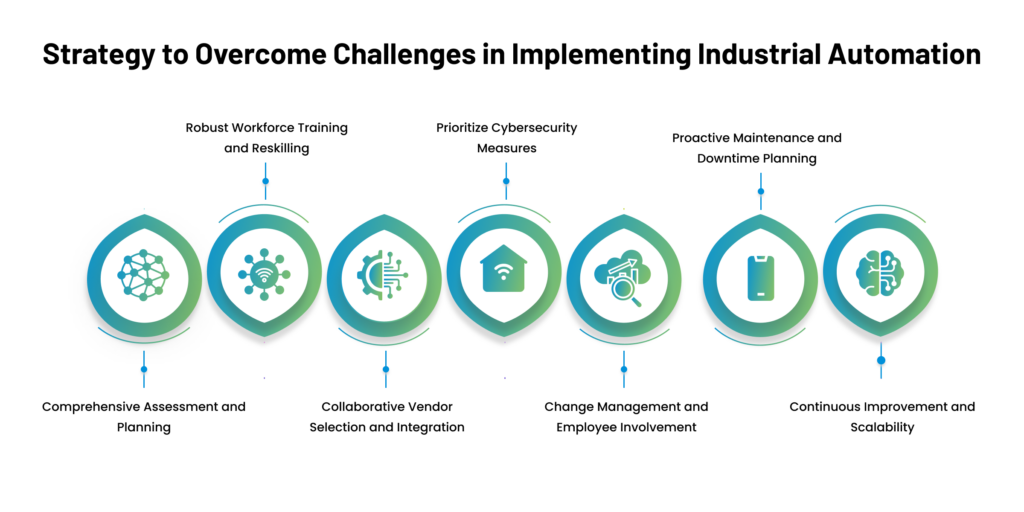
To overcome the challenges of implementing industrial automation in manufacturing, organizations can follow a strategic approach that involves seven key steps. Each step addresses specific aspects of the challenges and aims to create a comprehensive and successful automation implementation plan:
By following this comprehensive seven-step strategy, organizations can overcome the challenges of implementing industrial automation in manufacturing. This approach emphasizes the importance of people, technology, and processes working harmoniously to achieve successful automation integration and drive long-term benefits for the organization.
Manufacturing automation presents significant challenges and promising opportunities for organizations striving to stay competitive in an ever-evolving global landscape. Throughout this blog, we explored the significant hurdles companies may encounter when implementing automation and identified a seven-step strategy to overcome these obstacles.
Businesses can set the stage for a seamless transition to automation by conducting a thorough assessment and planning phase. Prioritizing the reskilling and training of the existing workforce ensures a more engaged and empowered workforce capable of leveraging the potential of automation to its fullest extent. Collaborative vendor selection and integration and a robust cybersecurity strategy safeguard the automation ecosystem from potential vulnerabilities.
Moreover, a strong emphasis on change management, involving employees in the decision-making process, fosters a positive and adaptable organizational culture that welcomes automation as a transformative force rather than a disruptive one. Proactive maintenance planning and downtime management guarantee the uninterrupted flow of production, maximizing the benefits of automation while minimizing potential risks.
As we move into the future, in addition to embracing future trends, organizations can further accelerate their journey toward successful industrial automation by partnering with digital transformation consulting firms. Partnering with a renowned digital transformation company can provide invaluable expertise and guidance, accelerating the successful implementation of automation and positioning businesses at the forefront of advanced manufacturing, ushering in a new era of smart, sustainable, and efficient manufacturing through industrial automation.